- Minimally Invasive: Small incisions are made to remove ovarian cysts with a laparoscope, offering less pain and faster recovery.
- Indications: Performed for functional cysts, dermoid cysts, endometriomas, or cystadenomas causing symptoms like pain or bloating.
- Procedure: Involves anesthesia, small incisions, gas insufflation for visibility, cyst removal, and closure of incisions.
- Benefits: Shorter recovery time (1-2 weeks), less scarring, preserved fertility (if ovaries are spared), and lower complication rates.
Laparoscopic Ovarian Cyst Surgery: Detailed Overview
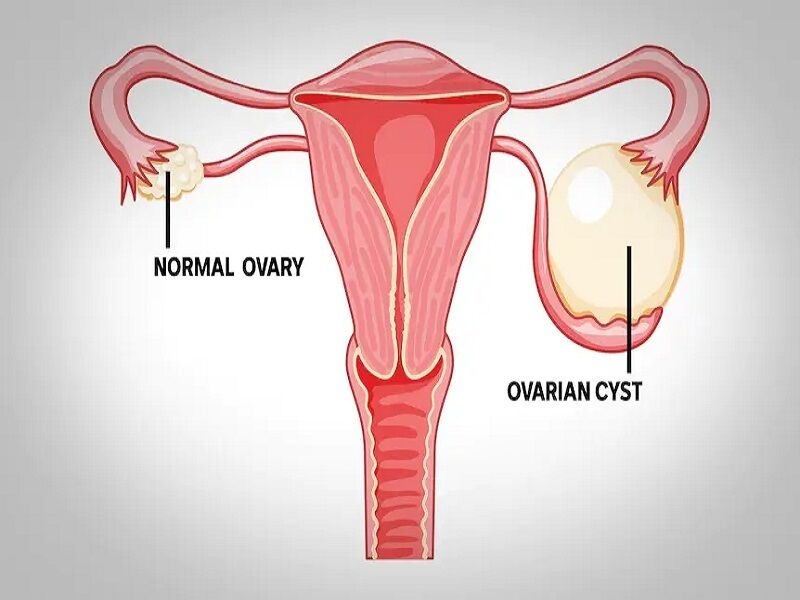
Laparoscopic ovarian cystectomy is a minimally invasive surgery used to remove ovarian cysts (fluid-filled sacs that develop on or in an ovary). The procedure involves making small incisions in the abdomen through which a laparoscope (a small camera) and other surgical tools are inserted to remove the cysts. This method is preferred over traditional open surgery due to its quicker recovery time, minimal scarring, and lower risk of complications.
🧬 What Are Ovarian Cysts?
Ovarian cysts are common, particularly in women of reproductive age. They can be:
- Functional cysts: The most common type, often related to the menstrual cycle.
- Dermoid cysts: Contain tissue like hair, skin, or teeth.
- Endometriomas: Caused by endometriosis, filled with old blood.
- Cystadenomas: Fluid-filled cysts that develop from the ovarian tissue.
Most cysts are benign (non-cancerous) but may cause symptoms such as:
- Pelvic pain or discomfort
- Irregular periods
- Bloating or fullness
- Pain during intercourse
- Urinary or bowel changes
- If large, cysts may also lead to torsion (twisting) of the ovary or rupture, both of which are medical emergencies.
🛠️ Procedure Steps for Laparoscopic Ovarian Cystectomy
- Anesthesia: The procedure is performed under general anesthesia, ensuring that the patient is asleep and pain-free.
- Incisions: The surgeon makes two to four small incisions (around 0.5 to 1 cm each) in the lower abdomen. One incision is used for the laparoscope (camera), while the others are for surgical tools.
- Gas Insufflation: Carbon dioxide (CO₂) gas is used to inflate the abdomen, which provides more space and improves visibility for the surgeon.
- Cyst Removal: The laparoscope is inserted to allow visualization of the cyst. Depending on the cyst’s size and location, the surgeon may:
- Remove the cyst intact (if it is small and easily accessible).
- Drain the cyst (for larger cysts), and then remove the empty cyst sac.
- Ovary Preservation: The surgeon carefully removes the cyst while aiming to preserve the surrounding ovarian tissue. In some cases, if the cyst is large or malignant, part of the ovary may need to be removed.
- Closure: After removing the cyst, the surgeon will inspect the area for any other issues. The incisions are then closed with sutures or surgical glue.
🕒 Duration and Recovery
- Surgery Duration: The procedure typically takes 30 minutes to 1 hour, depending on the size and complexity of the cyst.
- Hospital Stay: Most patients can go home the same day or after a one-night stay, depending on their condition.
- Recovery Time: Recovery is generally quick (typically 1-2 weeks for most women). Pain and discomfort are usually mild and can be managed with pain relievers.
- Return to Normal Activity: Most women can return to light activity within a few days and full activity (including exercise) after 4-6 weeks.
✅ Benefits of Laparoscopic Ovarian Cystectomy
- Minimally invasive with smaller incisions, reducing scarring and pain.
- Faster recovery and shorter hospital stay compared to traditional open surgery.
- Preservation of fertility by avoiding the removal of healthy ovarian tissue.
- Lower risk of infection and blood loss.
- Quicker return to normal life and minimal disruption to daily activities.
⚠️ Risks and Complications
While laparoscopic ovarian cystectomy is generally safe, there are some risks, including:
- Infection at the incision sites.
- Bleeding during or after surgery.
- Damage to surrounding organs (e.g., bowel, bladder, or other ovary).
- Ovary damage or loss, especially if cysts are very large or complicated.
- Cyst recurrence: In some cases, cysts may come back, particularly if only part of the cyst was removed.
- Anesthesia complications: As with any surgery involving anesthesia, there are risks, though these are minimal.
🧪 Post-Operative Care
- Pain Management: Mild to moderate pain is common after the procedure, which can be managed with over-the-counter pain relievers or prescribed medication.
- Diet: Patients are typically advised to start with liquids and progress to solid food after the procedure.
- Activity: Light walking is encouraged to prevent blood clots, but heavy lifting and strenuous activities should be avoided for about 4-6 weeks.
- Follow-Up: A follow-up appointment is usually scheduled within 1-2 weeks to ensure proper healing and to discuss the pathology results (if the cyst was sent for testing).
👶 Fertility Considerations
- Laparoscopic ovarian cystectomy generally preserves fertility because it allows the surgeon to carefully remove the cyst while leaving the surrounding healthy ovarian tissue intact.
- If the cyst is large, recurrent, or cancerous, it may require the removal of the affected ovary, which can affect fertility, but this is only done when absolutely necessary.
❗ When Laparoscopic Ovarian Cystectomy May Not Be Suitable
- Large or complex cysts: If the cyst is too large, adherent to other organs, or has suspicious features, it may not be suitable for a laparoscopic approach.
- Cancerous cysts: If a cyst is found to be cancerous, a more extensive surgery, such as open surgery, may be necessary.
- Previous abdominal surgery: Significant scarring from past surgeries may make the procedure more difficult or increase the risk of complications.
🧾 Conclusion
Laparoscopic ovarian cystectomy is a highly effective, minimally invasive method to remove ovarian cysts with the benefits of faster recovery, less pain, and smaller scars compared to traditional open surgery. It is particularly beneficial for women looking to preserve their fertility, as it minimizes damage to the ovaries. However, careful evaluation of the cyst’s size, location, and nature is necessary to determine if laparoscopic surgery is the best option.

