- Uterine fibroids are non-cancerous growths in or on the uterus.
- They are common in women of reproductive age, especially over 30.
- Symptoms may include heavy periods, pelvic pain, bloating, and frequent urination.
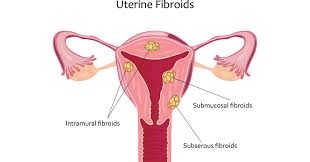
- Types include intramural, subserosal, submucosal, and pedunculated fibroids.
- Diagnosis is done via ultrasound, MRI, or pelvic exam.
- Treatments include medications, surgery (myomectomy/hysterectomy), or UAE (uterine artery embolization).
Absolutely! Here’s a detailed overview of Uterine Fibroids, also known as leiomyomas or myomas — one of the most common conditions affecting women of reproductive age.
🌸 What Are Uterine Fibroids?
Uterine fibroids are non-cancerous (benign) tumors that grow in or on the uterus. They are made of smooth muscle and fibrous tissue and can vary in size from tiny (pea-sized) to large masses that can distort the shape of the uterus.
🧭 Types of Uterine Fibroids
- Intramural Fibroids:
- Grow within the uterine wall
- Most common type
- Can enlarge and distort the uterus
- Subserosal Fibroids:
- Grow on the outer surface of the uterus
- Can press on nearby organs (e.g., bladder)
- Submucosal Fibroids:
- Grow into the uterine cavity
- Can cause heavy bleeding and fertility issues
- Pedunculated Fibroids:
- Grow on a stalk either outside or inside the uterus
- Can twist and cause pain
📊 How Common Are They?
- Affect up to 70–80% of women by age 50
- More common in:
- Women of African descent
- Women with a family history of fibroids
- Those with early menstruation or high estrogen exposure
⚠️ Symptoms of Fibroids
Many women have no symptoms, but when they occur, they may include:
- Heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding
- Pelvic pressure or pain
- Frequent urination
- Difficulty emptying the bladder
- Constipation
- Pain during sex
- Lower back or leg pain
- Infertility or miscarriage (in some cases)
- Abdominal bloating or a visible bulge
🧬 Causes and Risk Factors
Exact cause is unknown, but factors include:
- Hormones: Estrogen and progesterone promote fibroid growth
- Genetics: Family history increases risk
- Race: Higher risk in Black women
- Obesity and diet (high red meat, low greens)
- Vitamin D deficiency
- Environmental factors
🩺 Diagnosis
- Pelvic exam
- Ultrasound: Transabdominal or transvaginal
- MRI: For size, number, and location
- Sonohysterography: Uses saline to better visualize fibroids inside uterus
- Hysteroscopy: A small camera inserted into the uterus
- Laparoscopy: For large or hidden fibroids
💊 Treatment Options
Depends on size, location, symptoms, and fertility goals.
🔹 Medications
- NSAIDs: For pain
- Hormonal therapies:
- Birth control pills/patches
- GnRH agonists (e.g., leuprolide)
- Progestin-releasing IUD (e.g., Mirena)
- Tranexamic acid (for heavy bleeding)
🔸 Minimally Invasive Procedures
- Uterine artery embolization (UAE): Cuts off blood supply to shrink fibroids
- MRI-guided focused ultrasound: Destroys fibroid tissue
- Endometrial ablation: Destroys the lining of the uterus (not for women wanting pregnancy)
🔺 Surgical Treatments
- Myomectomy: Surgical removal of fibroids (uterus preserved)
- Hysterectomy: Complete removal of the uterus (curative but ends fertility)
🌱 Natural and Lifestyle Approaches
- Weight management
- Diet rich in vegetables and low in red meat
- Regular exercise
- Vitamin D supplementation
- Stress reduction
👶 Fibroids and Fertility
- Can interfere with implantation, sperm movement, or fetal growth
- Submucosal fibroids are most associated with fertility problems
- Myomectomy may improve chances of conception in some cases
🔄 Fibroids vs. Adenomyosis
| Feature | Fibroids | Adenomyosis |
|---|---|---|
| Tissue Type | Muscle and fibrous tissue | Endometrial tissue in uterine muscle |
| Growth Location | Inside/on uterus | Inside uterine wall |
| Shape | Discrete masses | Diffuse thickening |
| Fertility Impact | May interfere with pregnancy | Can affect implantation |
| Cure | Hysterectomy (if severe) | Hysterectomy (if severe) |
Would you like a visual chart, infographic, or a guide to natural remedies or diet tips for fibroids?

